Apr 8, 2025
What is a Mark-to-Market Valuation?
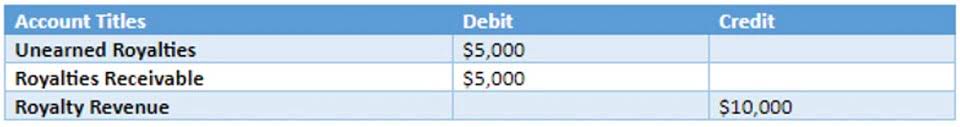
MTM accounting provides mark to market accounting transparency but can magnify reported losses during market downturns. For example, suppose a bank holds a portfolio of mortgages, and the housing market begins to crash. This would require the bank to mark down these assets to their current market value, potentially reducing its equity base significantly—even if the bank plans to hold these assets long-term. This article explored the definition, history, purpose, application, criticisms, and examples of mark to market accounting.
How Does One Mark Assets to Market?
Available for sale securities are the most common example of mark to market accounting. An available-for-sale asset is a financial security that can either be in debt or equity purchased to sell the securities before it reaches maturity. In cases of securities that do not have a maturity, these securities will be sold before a long period for which these securities are generally held.

Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Mark-to-Market Accounting

Simply multiply these differences by the number of shares for the total MTM gain or loss. It cultivates a truer valuation that can protect and inform investors, providing a real-time financial map, which is crucial for making informed decisions. It also aligns accounting practices with today’s fast-moving markets, so companies using MTM are less likely to find themselves with vastly outdated valuations. If a company’s stock is trading higher today than when it was purchased, MTM accounting will adjust the book value upwards, potentially beefing up an investor’s equity. If the market is having a bad day and stock prices plummet, those same stocks shrink in value on paper almost instantly, thanks to MTM. In line with this accounting rule, the debate over the application of mark-to-market, especially during financial turmoil, underscores the significance of GAAP and FASB’s guidance.
How to Mark Assets to Market?
- In personal accounting, the market value is the same as the replacement cost of an asset.
- It’s easy for accountants to estimate the market value if traders buy and sell that type of asset often.
- The Enron scandal and its subsequent downfall is the stock market drama of the last several decades.
- If the current market price is higher than the purchase price, the asset has a gain.
- However, its malleability is a double-edged sword, given that it can also be used to deceptively hide true values from investors and creditors.
- For example, a real estate property may have a historical value of $100,000 but may be worth $1,000,000 (by marking the value to market, the books will show $1,000,000 today as opposed to $100,000).
- Since MTM values assets based on current market prices, significant changes can lead to amplified gains or losses, creating a feedback loop that can exacerbate market volatility.
Our team will use its expertise to create a tax plan that supports the goals of your business for many years to come. But there is Opening Entry not a liquid market for this bond like there is for Treasury notes. As a result, an accountant would start with the bond’s value based on Treasury notes. He would reduce the bond’s value, based on its risk as determined by a Standard and Poor’s credit rating. To estimate the value of illiquid assets, a controller can choose from two other methods.
What is a Three White Soldiers Candlestick Pattern?
- Our team will use its expertise to create a tax plan that supports the goals of your business for many years to come.
- Six months later when Jim sells the shares, they are trading at $500, so that means he has lost $10,000.
- In futures trading, marking to market (MTM) is the daily valuation of open futures contracts to reflect their current market value.
- Thus, the above are some important differences between the two types of methods used to record the assets and liabilities.
- Mark-to-market (MTM) values assets and liabilities based on their current market prices.
- In simple terms, mark to market refers to measuring or evaluating the fair value of the assets and liabilities of a company, which is subject to periodic fluctuations.
- If a margin call is necessary, the trader will receive a notice to deposit the necessary funds to cover the shortfall in his or her investment portfolio.
During the 2020 pandemic, many airlines had significant MTM losses on fuel hedges when oil prices collapsed, creating financial reporting challenges even as their actual operations benefited from lower fuel costs. For hedge funds and private equity firms, MTM becomes more complex since they tend to have more Level 3 assets. A venture capital firm investing in startups might mark its portfolio companies retained earnings balance sheet to value based on the most recent funding round prices. Level 1 assets have readily observable market prices, like publicly traded stocks on major exchanges. If you own shares of Apple Inc. (AAPL), for instance, determining their value is as simple as checking the latest trading price.
More Details